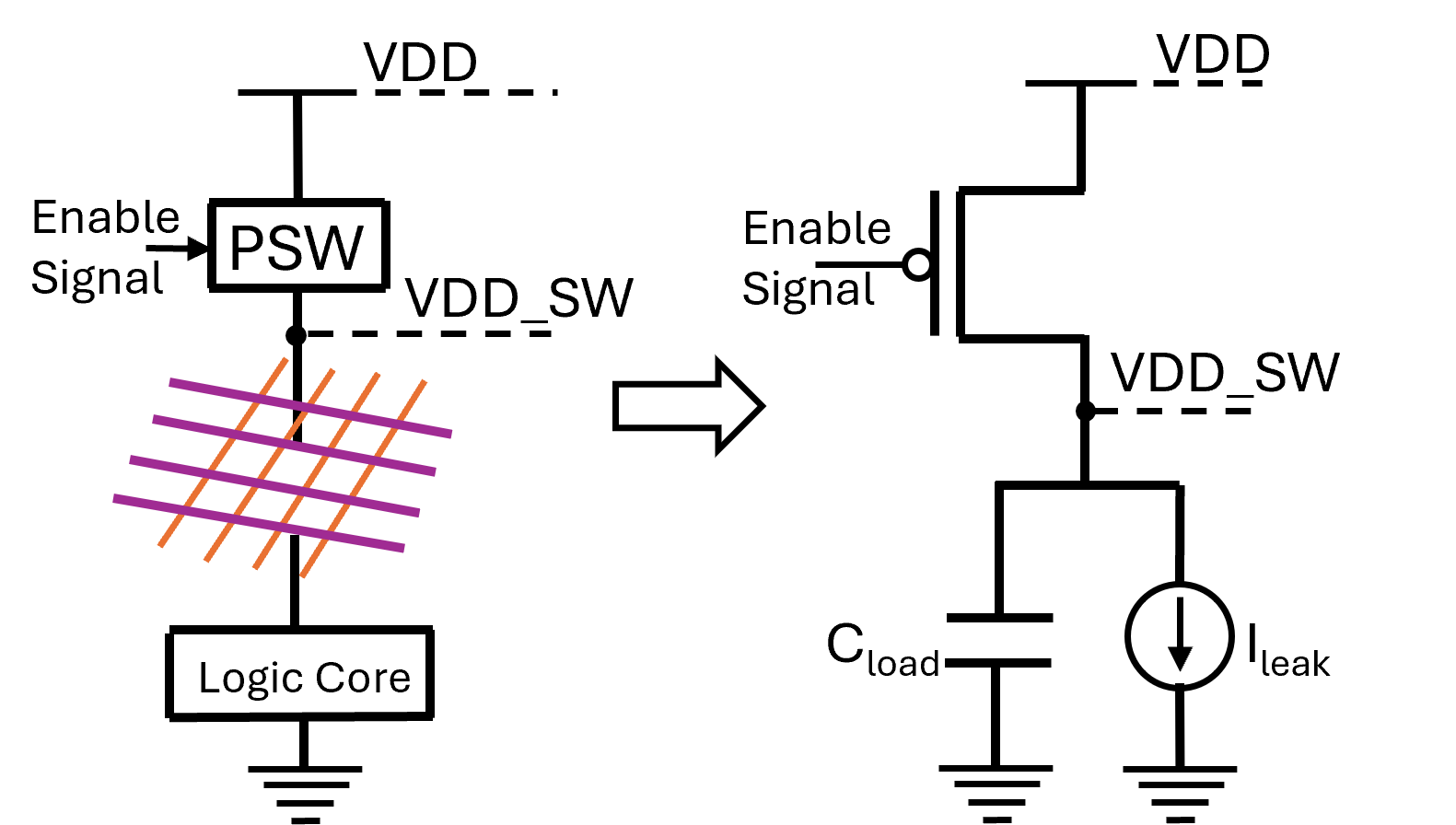ML-INSIGHT: Machine Learning for Inrush Current Prediction and Power Switch Network Improvement
Authors
V. Gopalakrishnan, B.-Y. Wu, and V. A. Chhabria
Abstract
Today’s large-scale designs utilize power gating to achieve low power consumption. This strategy involves creating an efficient power switch network that considers both the surge current (inrush) and the time it takes for the domain to wake up (wakeup latency). Optimized design of the power switch network requires an approach that minimizes the inrush current while meeting the wakeup latency specification. However, analyzing the network for inrush is computationally very expensive with large runtimes, particularly for complex networks, making an optimization framework that calls the analysis engine under the hood prohibitively slow. To address this challenge, this paper introduces the use of machine learning (ML) techniques to estimate inrush current. The ML-enabled fast inference for inrush prediction is applied to optimize the power switch network to minimize the inrush current and also meet the wakeup latency constraint. The ML model demonstrates a mean error of 5% compared to SPICE simulations, offering an acceleration of over 50X.